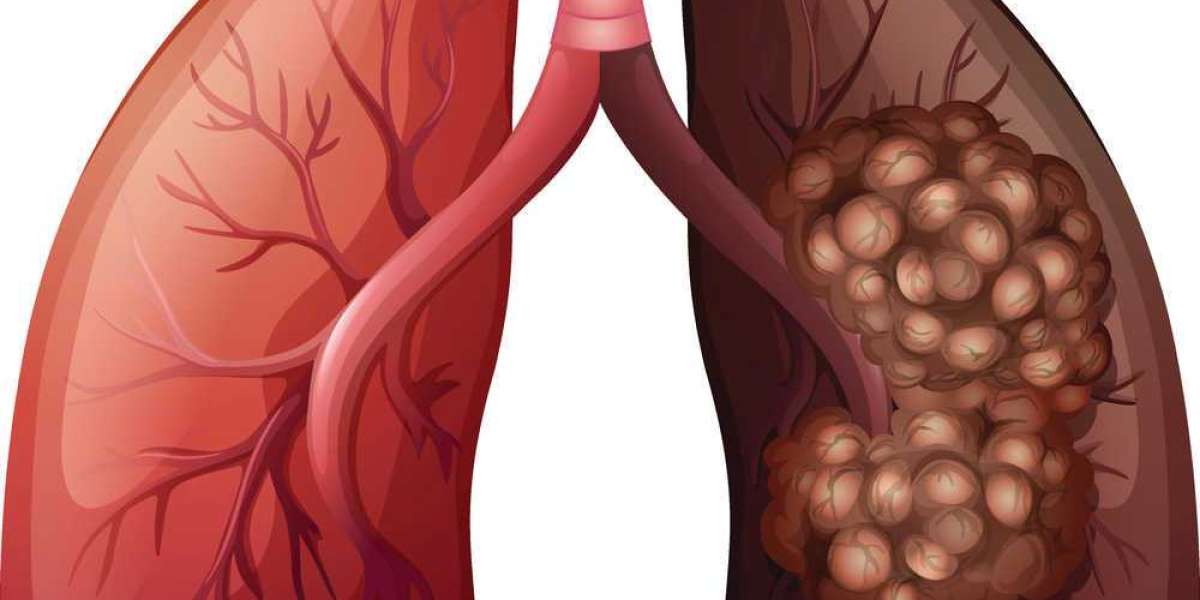
Unchecked cell development in the lung tissues is a hallmark of lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma. Malignant lung tumors come in two main types: small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). The most noticeable symptoms include shortness of breath, chest discomfort, weight loss, and coughing up blood. Long-term tobacco use is the primary cause of lung cancer, accounting for 85% of cases. Ten to fifteen percent of cases include people who have never smoked before. A combination of genetic predispositions plus exposure to toxic gases, such as radon gas, secondhand smoke, asbestos, or other air pollutants, is frequently the cause of many cases. Ten to thirty percent of lung adenocarcinomas are caused by mutations in the K-ras proto-oncogene. Roughly 4 percent of non-small-cell lung cancers are thought to have an EML4-ALK tyrosine kinase fusion gene involved. In primary lung cancer, tumor markers like CYFRA 21-1 and CEA are very useful for diagnosis.
For more: lung cancer antibody