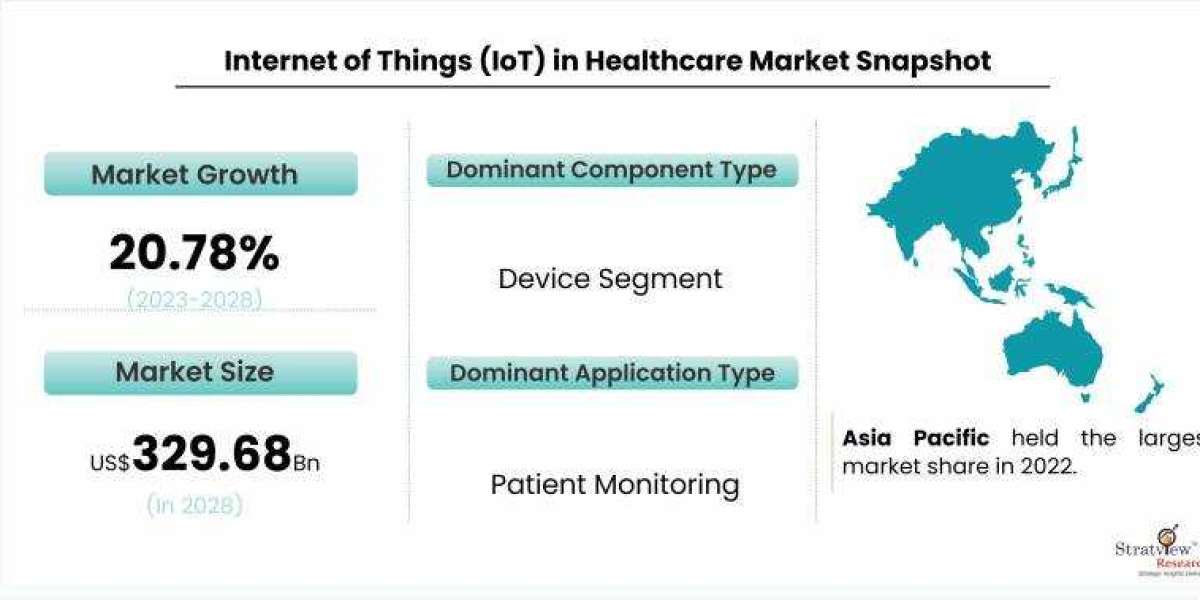
In recent years, the combination of the Internet of Things (IoT) and telemedicine has emerged as a powerful force in revolutionizing healthcare delivery. The ability to connect medical devices, collect real-time data, and enable remote consultations has transformed the way healthcare is delivered to patients, especially in remote or underserved areas. In this article, we will explore how IoT and telemedicine are transforming remote healthcare delivery. The IoT in healthcare market is estimated to grow from USD 106.17 billion in 2022 to USD 329.68 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 20.78% during the forecast period.
Telemedicine, the use of technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, has gained significant traction in recent years. IoT has played a vital role in expanding the capabilities and reach of telemedicine. Through the integration of IoT devices and sensors, patients can now be remotely monitored, and healthcare professionals can access real-time patient data from a distance.
One of the key applications of IoT in telemedicine is remote patient monitoring. IoT-enabled devices, such as wearable sensors and home monitoring systems, can continuously collect data on vital signs, medication adherence, and disease-specific parameters. This data is transmitted securely to healthcare providers, who can monitor patients' health status remotely. Remote patient monitoring is particularly valuable for individuals with chronic conditions or those recovering from surgeries, as it allows for proactive intervention and reduces the need for frequent hospital visits.
IoT also enables the seamless integration of medical devices and electronic health records (EHR) systems in telemedicine. By connecting devices such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and EKG machines to IoT platforms, healthcare professionals can access real-time data directly within the patient's EHR. This integration eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances the efficiency of telemedicine consultations. Healthcare providers can make more informed decisions based on up-to-date patient data, even in remote settings.
In addition to remote patient monitoring, IoT enhances telemedicine consultations through the use of video conferencing and connected devices. With IoT-enabled telemedicine solutions, patients can have virtual consultations with healthcare professionals, eliminating the need for in-person visits, especially for routine check-ups and follow-ups. IoT devices, such as digital stethoscopes, otoscopes, and high-resolution cameras, can be used by patients under the guidance of healthcare professionals to capture and transmit clinical data during virtual consultation. This real-time visual and audio data allows healthcare providers to assess patients remotely, diagnose conditions, and provide appropriate treatment plans.
Moreover, IoT enables telemedicine to extend beyond traditional healthcare settings into patients' homes. With the rise of remote patient monitoring and connected devices, individuals can receive care in the comfort of their own homes. This is especially beneficial for patients with limited mobility, chronic conditions, or those living in remote areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. IoT and telemedicine bring healthcare services closer to patients, improving accessibility and reducing healthcare disparities.
The integration of IoT in telemedicine does come with its challenges. Privacy and security of patient data are of paramount importance. Healthcare organizations must ensure that patient data transmitted over IoT platforms is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, is crucial to maintain patient trust and confidentiality.
Interoperability and standardization are also critical for the seamless integration of IoT devices and telemedicine platforms. Efforts are underway to establish common standards and protocols, such as HL7 FHIR and DICOM, to enable interoperability and ensure the exchange of data between different devices and systems. Collaboration among stakeholders, including healthcare providers, technology companies, and regulatory bodies, is essential to drive the widespread adoption of interoperable IoT-enabled telemedicine solutions.
In conclusion, IoT and telemedicine are transforming remote healthcare delivery by enabling remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and home-based care. Through the integration of IoT devices, healthcare professionals can access real-time patient data and provide timely interventions. The combination of IoT and telemedicine expands access to healthcare services, improves patient outcomes, and enhances the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in IoT-enabled telemedicine, driving a new era of remote healthcare.