Introduction
In today's fast-paced world, where innovation is the driving force behind technological advancements, Electroactive Polymers (EAP) have emerged as a groundbreaking and transformative class of materials. EAPs represent a convergence of materials science and electronics, offering unprecedented potential across a wide range of industries. As the world transitions towards more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions, EAPs are playing a pivotal role in reshaping the future. In this article, we will delve into the Electroactive Polymers market, exploring its current state, applications, and the immense potential it holds.
Understanding Electroactive Polymers (EAP)
Electroactive Polymers, often referred to as smart polymers, are materials that can change their shape or properties in response to an external electrical stimulus. This remarkable behavior is made possible by the incorporation of conductive or semi-conductive elements within a polymer matrix. The resulting composite materials exhibit a wide range of properties such as flexibility, light weight, and the ability to generate mechanical motion when subjected to electrical fields or voltage changes.
Market Overview
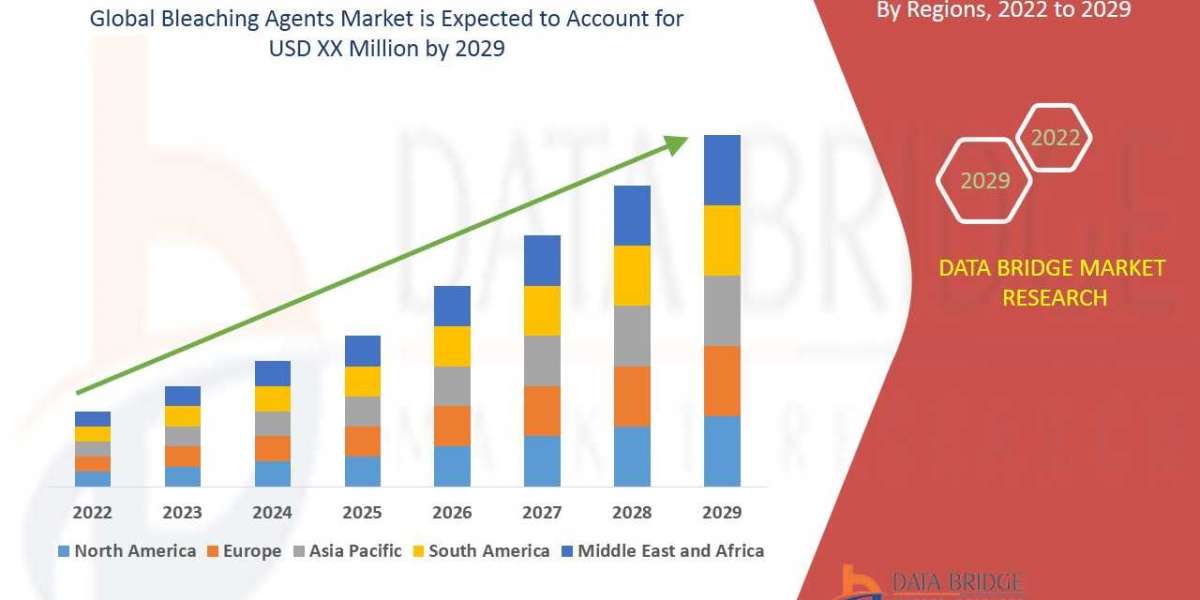
The global Electroactive Polymers market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years and is poised for even greater expansion in the coming years. Several factors contribute to this growth, including increasing investments in research and development, rising demand for lightweight and flexible materials, and the push for more sustainable technologies.
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, the global EAP market was estimated to be valued at around $4.2 billion. However, it's essential to note that the market size may have significantly grown since then, given the increasing adoption of EAPs across various industries.
Applications of Electroactive Polymers
- Actuators and Sensors: One of the primary applications of EAPs is in the development of advanced actuators and sensors. These materials can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, making them ideal for creating responsive and precise actuators. They find applications in robotics, medical devices, haptic feedback systems, and more. In sensors, EAPs can be used for pressure, temperature, and strain sensing.
- Artificial Muscles: EAPs have gained recognition for their remarkable resemblance to natural muscles in terms of their response to electrical stimuli. This characteristic makes them invaluable in the field of robotics, where they are used to create lifelike and responsive movements in robotic systems.
- Energy Harvesting: EAPs have the potential to revolutionize the field of energy harvesting. They can capture energy from various sources, including vibrations and mechanical movements, and convert it into electrical energy. This application has significant implications for powering small electronic devices and sensors in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
- Medical Devices: EAPs are being explored for use in medical devices and prosthetics. Their flexibility and biocompatibility make them suitable for creating comfortable and responsive wearable medical devices, including smart bandages and assistive devices for individuals with mobility impairments.
- Soft Robotics: Soft robotics is a rapidly growing field, and EAPs are at the forefront of innovation in this domain. These materials enable the development of soft and flexible robots that can navigate complex environments, making them ideal for applications like search and rescue missions, minimally invasive surgery, and more.
- Aerospace and Automotive: The aerospace and automotive industries are increasingly adopting EAPs to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. EAP-based components can replace conventional mechanical systems, resulting in lighter and more energy-efficient aircraft and vehicles.
- Consumer Electronics: EAPs are finding their way into consumer electronics, enhancing user experiences through haptic feedback in touchscreens and wearable devices. This technology enables more immersive interactions with digital devices.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Electroactive Polymers hold immense promise, there are challenges that need to be addressed for their widespread adoption. These challenges include:
- Material Development: Developing EAPs with the right combination of properties, such as high actuation performance, durability, and environmental stability, can be challenging. Research and development efforts are focused on creating materials that meet these criteria.
- Cost: EAPs can be expensive to produce, limiting their use in cost-sensitive applications. As technology advances and production scales up, it is expected that costs will decrease, making EAPs more accessible.
- Durability: Ensuring the long-term durability of EAP-based systems, especially in harsh environments, is a critical concern. Ongoing research is addressing this issue to expand the range of applications.
Despite these challenges, the Electroactive Polymers market presents significant opportunities. The increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency is driving the demand for EAPs, especially in the aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. Moreover, ongoing research and innovation are likely to lead to breakthroughs that will expand the scope of EAP applications.
Key Market Players:
Some of the prominent players operating in the global electroactive polymers market are Solvay (Belgium), Parker-Hannifin Corporation (U.S.) Agfa-Gevaert Group (Belgium), 3M (U.S.), Merck Sharp Dohme Corporation (Germany), The Lubrizol Corporation (U.S.), NOVASENTIS, INC (U.S.), Premix (Finland), PolyOne Corporation (U.S.), and Kenner Material System Co., Ltd (China).
Conclusion
Electroactive Polymers represent a remarkable intersection of materials science and electronics, offering transformative capabilities across various industries. With applications ranging from robotics to healthcare, energy harvesting to aerospace, EAPs are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of technology.
As research and development efforts continue to advance, addressing challenges such as material development and cost, the Electroactive Polymers market is poised for substantial growth. This innovative class of materials holds the potential to usher in a new era of sustainable and energy-efficient technologies, making our world smarter, more responsive, and more connected than ever before.
About Market Research Future:
At Market Research Future (MRFR), we enable our customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through our Cooked Research Report (CRR), Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR), Raw Research Reports (3R), Continuous-Feed Research (CFR), and Market Research Consulting Services. MRFR team have supreme objective to provide the optimum quality market research and intelligence services to our clients. Our market research studies by Components, Application, Logistics and market players for global, regional, and country level market segments, enable our clients to see more, know more, and do more, which help to answer all their most important questions.
Contact:
Market Research Future®
99 Hudson Street,5Th Floor
New York, New York 10013
United States of America
Phone:
+1 628 258 0071(US)
+44 2035 002 764(UK)
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com